Sunny Series: SMA’s Insights on Home Energy and Solar Power Generation

SMA Home Energy Solutions proudly presents the Sunny Series, a beacon of knowledge illuminating the path toward energy independence through solar power generation for homes. Building upon over 40 years of experience as a market leader, this series will cultivate content comprising original insights, innovative ideas and practical applications. The first article of our Sunny Series, “SMA’s Insights on Home Energy and Solar Power Generation,” will serve as a foundation to understand the current PV market and where the industry is headed.
At the core of the Sunny Series is the goal to empower you with SMA’s knowledge of solar and renewable independence. Join the Sunny Series on this enlightening journey, and together, let’s unlock the potential of solar power generation for homes and seize control of our energy future.
In partnership with valued partners and customers, SMA is playing a pivotal role in shaping the energy transition for a future that is both environmentally conscious and sustainable. The company is delighted to present the Sunny Series by SMA Home Energy Solutions.
Empowering Energy Independence: Embracing Self-Consumption with Your Own Generated Energy
Self-consumption is using electrical power generated on-site to power loads on the same site rather than exporting excess power off-site. Put differently, a homeowner’s self-consumption involves utilizing the electricity generated by their PV system to meet their household’s energy needs. The power produced by a homeowners PV system is exclusively utilized by them.
For the purposes of this article, on-site means a home served by an electric utility, and off-site would mean anywhere else that electric utility serves. Usually this is a neighbor’s house!
Fostering Energy Autonomy: The Significance of Self-Consumption and Grid Energy Sales for Homeowners
What makes self-consumption important to a homeowner? In two words – saving money.
For many homeowners in the US, utility companies adjust electricity rates during certain times of the day. This is called a time-of-use (TOU) rate. Opting to draw electricity from the grid, especially during peak hours, has the potential to result in notably higher costs for homeowners on their utility bill. Those who choose to invest in a PV system as homeowners gain the advantage of avoiding these additional charges, enabling them to self-consume the solar electricity generated by their PV system. Most utilities in the US allow for excess PV power generated by a home PV system to be sent back (selling excess solar energy) through the home’s electric meter and then onto the utility conductors. This excess energy usually ends up powering some of the neighbor’s loads. Think of excess energy sent back to utility conductors as selling electricity back to the grid. The homeowner is then credited at some level for supplying the utility with this excess power that serves the neighbor.
As more and more homeowners install PV systems, utilities are changing the credit they provide for exported PV power. Additionally, to motivate homeowners to change demand patterns to avoid straining the grid at peak times, many utilities now charge customers different rates for consuming the same amount of energy depending on the time of day. Several TOU rate plans have very large differences in nighttime vs late afternoon rates.
Is There Ever a Time When Self-Consumption is Less Important?
The only time where self-consumption is not important is when the utility has a flat rate structure. In this case it does not matter what time of day the PV system produces. If the PV system produces right when a load needs power, this is beneficial for the homeowner. However, when the PV system produces solar electricity in the morning for afternoon energy needs, the utility’s morning credit helps balance the costs of using energy in the afternoon. Increasing self-consumption doesn’t improve the economics when utilities have a flat rate.
Please note, many utilities will at least have a seasonal (winter vs. summer) rate change if not time-of-use rates with two or three rates applying during each day, possibly mixed with seasonal changes as well. More and more utilities are moving away from a flat rate structure and implementing a seasonal structure and/or TOU rates.
How Can a Homeowner Increase Self-Consumption?
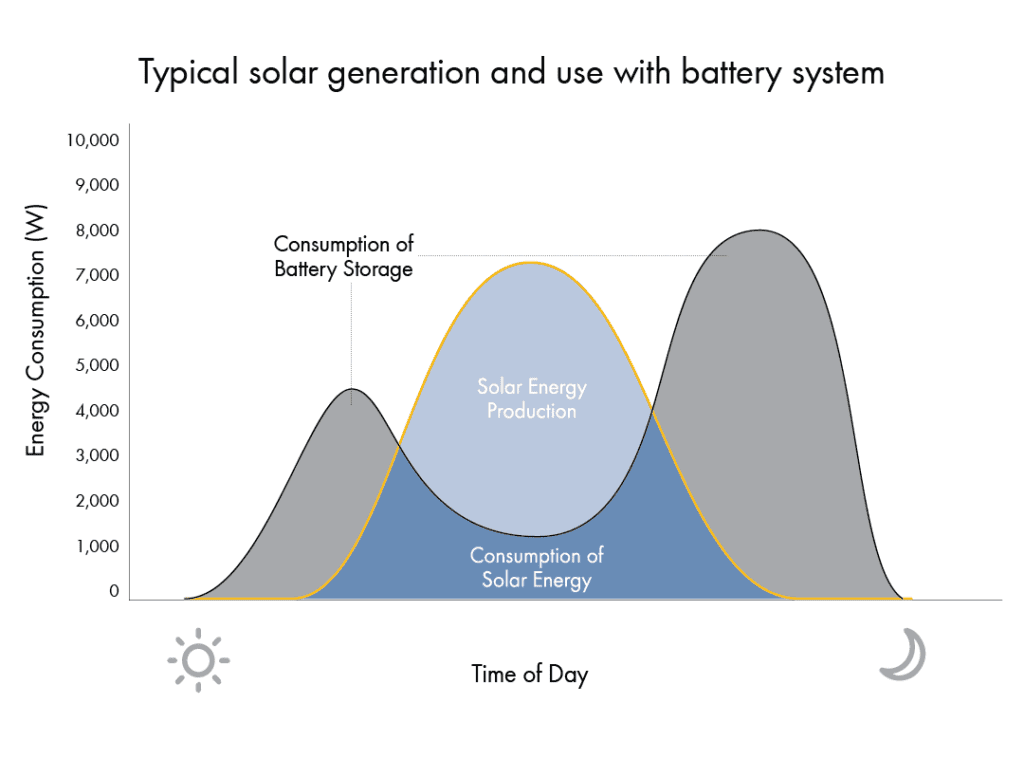
Another approach for increasing self-consumption is to include storage along with a PV system. The ability to store excess PV power in a battery dramatically increases self-consumption. Batteries allow homeowners to use and store power generated by their PV system. Rather than exporting excess power, the power is reserved in the battery. Batteries allow homeowners to access their solar energy for consumption at any time of the day. This is especially useful during grid outages or if the PV system does not produce when TOU rates are high. While batteries might come with a significant cost, the ability to utilize and store energy proves beneficial for homeowners looking for sustainable renewable energy.
Stay connected with us to discover more about achieving self-consumption with SMA’s Sunny Boy Smart Energy hybrid inverter.
*SMA Home Energy Solutions Product Manager, Robert Lamendola, and Marketing Program Manager, Diana Lamadora, contributed to this article.




Feel free to contribute!